The fact that perceptions affect safety cultures is undeniable, yet the best intending organizations often pay little attention to perceptions and the conditioning affect they have on new employees or the company. Whether accurate or not, perceptions become culturally-norming beliefs. When these common beliefs are combined with unclear values, potentially negative attitudes, and hypercompetitive priorities, a dangerous mixture of influences is placed on individuals attempting to solve problems in day-to-day operations. The need to understand perceptions and what drives them is critical.
Many organizations measure perceptions, but few effectively manage them. There are two types of perceptions: accurate and inaccurate. Which ones are you responding to? Perceptions are influenced by multiple sources, both internal and external. Unmanaged perceptions negatively affect safety communication. Even worse, they have been identified as contributing factors in multiple catastrophic incidents.
Culture is made up of common practices, attitudes, and perceptions of risks that influence behavioral choices at work and away from work. Culture is also influenced by management, leadership, supervision, workplace conditions, and logistics. Measuring a culture involves a complex metric of perceptions, workplace realities, past accident history, and inter-connectivity of the people.
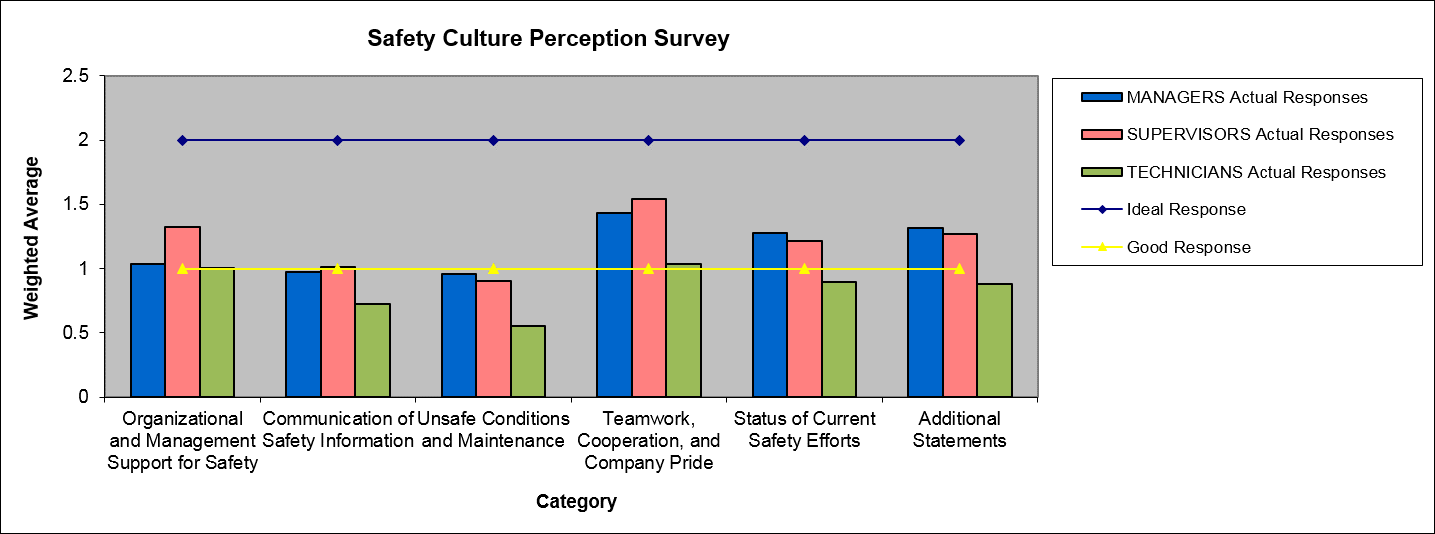
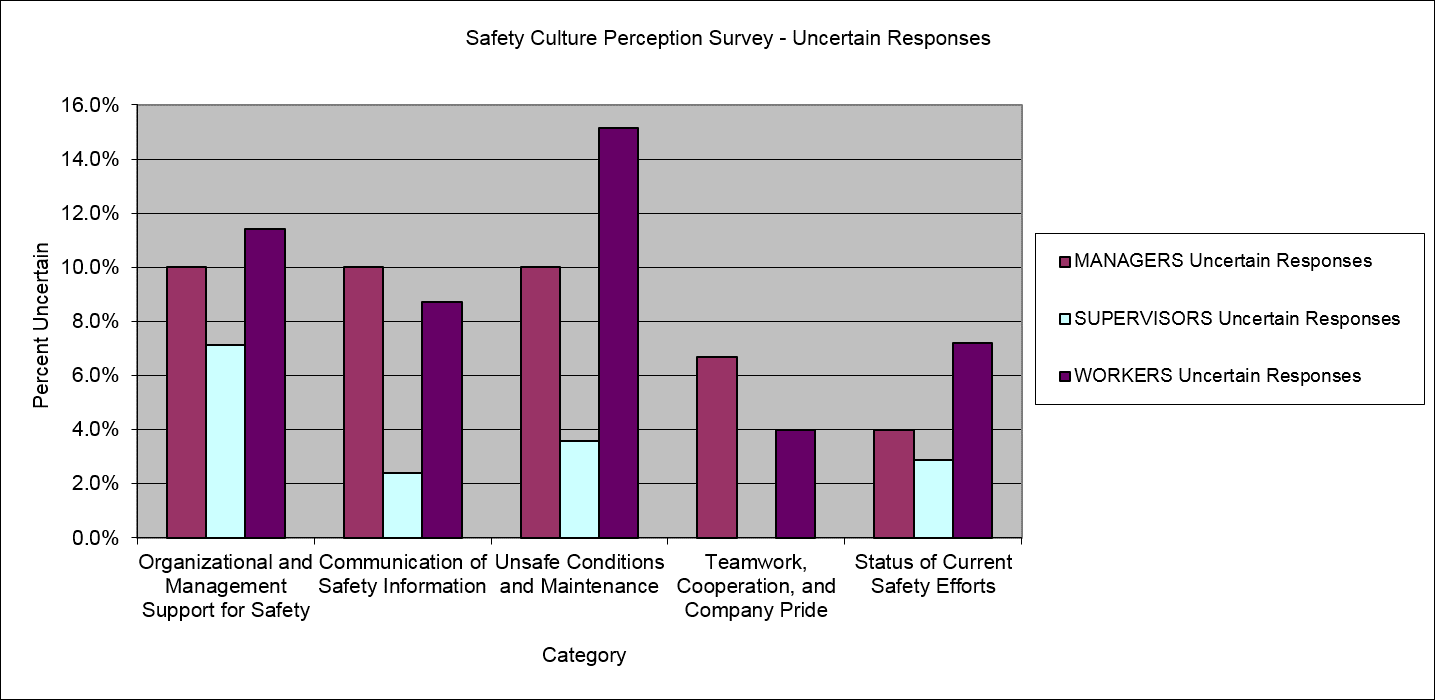
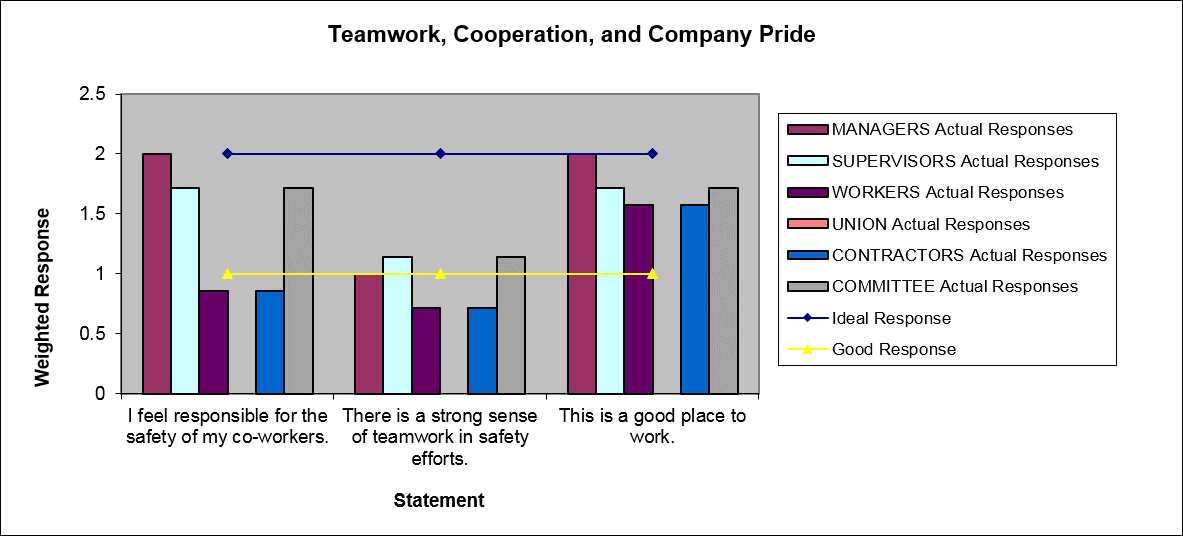
Perceptions are an important consideration when determining methods to improve safety or other aspects of performance. Perceptions affect behaviors, and they should be measured to determine a starting place for cultural modification efforts. Perception surveys can help identify areas for improvement and can serve as a baseline for measuring the effectiveness of improvement efforts.